Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sasaki, Yuji; Morita, Keisuke; Saeki, Morihisa*; Hisamatsu, Shugo*; Yoshizuka, Kazuharu*
Proceedings of 21st International Solvent Extraction Conference (ISEC 2017) (Internet), p.131 - 134, 2017/11
Three tridentate extractants including soft and hard donor has been developed and examined. The extractants are termed as 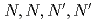 -tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA), methylimino-
-tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA), methylimino-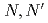 -dioctylacetamide (MIDOA) and
-dioctylacetamide (MIDOA) and 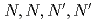 -tetraoctyl-thiodiglycolamide (TDGA). The results of the present study show that TODGA can extract completely lanthanides and actinides, MIDOA can extract palladium, technetium, and rhenium, and TDGA can extract palladium, silver, and gold. We can compare the distribution ratios of these metals by TODGA, MIDOA, and TDGA. These results can be supported by some spectrometric studies, i.e., IR, NMR and UV, and calculations of metal complexes.
-tetraoctyl-thiodiglycolamide (TDGA). The results of the present study show that TODGA can extract completely lanthanides and actinides, MIDOA can extract palladium, technetium, and rhenium, and TDGA can extract palladium, silver, and gold. We can compare the distribution ratios of these metals by TODGA, MIDOA, and TDGA. These results can be supported by some spectrometric studies, i.e., IR, NMR and UV, and calculations of metal complexes.
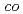 -tetrafluoroethylene) films using different media
-tetrafluoroethylene) films using different mediaNuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; et al.
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 40(4), p.359 - 362, 2015/12
The ion-track grafting of a vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film is necessary for preparing nanostructured hydroxide-ion-conductive electrolyte membranes. A key for success here is to obtain as high graft levels as possible (for higher conductivity) in a smaller number of tracks (for improving the other membrane properties). To this end, therefore, the effect of the medium for the VBC grafting was investigated as part of our continuing effort to optimize the experimental conditions. A 25  m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60
Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60 C. A medium was a mixture of water (H
C. A medium was a mixture of water (H O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H
O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H
O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
Shiga, Motoyuki; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki
Chemical Physics Letters, 378(5-6), p.539 - 547, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:21.52(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Umebayashi, Tsutomu; Sumita, Taishi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.254 - 258, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:136 Percentile:98.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)Single crystalline titanium dioxide (TiO ) rutile were implanted with 200keV F
) rutile were implanted with 200keV F at a nominal fluence of 1
at a nominal fluence of 1 10
10 to 1
to 1 10
10 ions cm
ions cm and then thermally annealed in air up to 1200
and then thermally annealed in air up to 1200 for 5h. The radiation damage and its recovery during the subsequent annealing were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry in channeling geometry and variable-energy positron annihilation spectroscopy. The lattice disorder was completely annealed at 1200
for 5h. The radiation damage and its recovery during the subsequent annealing were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry in channeling geometry and variable-energy positron annihilation spectroscopy. The lattice disorder was completely annealed at 1200 by the diffusion of point defects to the surface acting as a sink. According to the secondary ion mass spectrometry, the F depth profile was shifted to a shallower region along with the damage recovery, finally producing an F-doped layer where the impurity concentration increased steadily towards the surface. The F doping proved to provide a small modification to the conduction-band edge of TiO
by the diffusion of point defects to the surface acting as a sink. According to the secondary ion mass spectrometry, the F depth profile was shifted to a shallower region along with the damage recovery, finally producing an F-doped layer where the impurity concentration increased steadily towards the surface. The F doping proved to provide a small modification to the conduction-band edge of TiO , as assessed by theoretical band calculations.
, as assessed by theoretical band calculations.
Hirade, Tetsuya
Hoshasen Kagaku, (75), p.46 - 51, 2003/03
Enhancement of positronium (Ps) formation at low temperatures has been observed in many materials since 1980's. There were some interpretations. However, none of them explained the phenomena successfully. In 1998, a new idea of the Ps formation was proposed and the expected phenomena were successfully observed. This new Ps formation process will be explained with those experimental results and the possibility of usage of Ps formation for radiation chemistry researches will be also discussed.
JNC TN8400 2000-030, 17 Pages, 2000/12
As a representative of natural marine groundwater, the author selected pumped water from a Quaternary sedimentary aquifer of the Mobara gas-field in Japan and measured the concentration of total organic carbon (TOC) and of organic acid anions (formic, acetic, lactic, succinic, humic, fulvic, propionic, valeric and butyric acids). The concentration of TOC ranged from 22 1 to 24
1 to 24 0mg/L. As organic acid anions, only succinic and fulvic acids were detected and each concentration was given to be from 5.8
0mg/L. As organic acid anions, only succinic and fulvic acids were detected and each concentration was given to be from 5.8 0.5 to 8.3
0.5 to 8.3 0.3 and from 3.3
0.3 and from 3.3 0.2 to 3.5
0.2 to 3.5 0.2mg/L, respectively. By consideration of the temperature and the [SO
0.2mg/L, respectively. By consideration of the temperature and the [SO
 ] of the groundwater, it is inferred that the organic acid has been significantly decomposed by activities of microbes, such as the fermentation process, CH
] of the groundwater, it is inferred that the organic acid has been significantly decomposed by activities of microbes, such as the fermentation process, CH COO
COO + H
+ H O = HCO
O = HCO
 + CH
+ CH .
.
 W
W O
O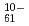 , P
, P W
W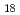 O
O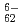 , SiW
, SiW O
O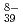 , by TBP
, by TBPAsakura, Toshihide; Donnet, L.*; Picart, S.*; Adnet, J.-M.*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 246(3), p.651 - 656, 2000/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.85(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Shibata, Toshio*; Haruna, Takumi*; Fujimoto, Shinji*; Zhang, S.*
JAERI-Tech 2000-061, 38 Pages, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Kumagai, Mikio*
JNC TJ9400 2000-002, 80 Pages, 2000/02
In order to develop an economically efficient wet separation process other than solvent extraction for reprocessing spent FBR-fuel (MOX fuel), we have investigated the possibility of an advanced ion exchange process. Based on the fundamental research results, we proposed an advanced ion exchange process considering the characteristics of FBR-fuel cycle. The separation system consists of a main separation process using a novel anion exchanger which has a rapid kinetics and two extraction chromatography processes for minor actinides isolation using novel impregnation adsorbents with high selectivity. The chemical flow sheet, mass balance chart, list of main equipment and installation layout of each equipment were estimated and designed for the process in a reprocessing plant with the capacity of 200 tHM/y FBR-fuel. The process was pfeliminarny evalualed from the aspects of economy performance, recovery of potentially useable resources, minimization of environmental risk and proliferation-resistance by comparing with the advanced PUREX process. Furthermore, the subjects which are important for the practical application of the process are also listed.
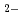 anions in solid parahydrogen; Effect of nuclear spins on chemical reactions
anions in solid parahydrogen; Effect of nuclear spins on chemical reactionsKumada, Takayuki; *; *; *; Aratono, Yasuyuki; Miyazaki, Tetsuro*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 101(7), p.1198 - 1201, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:40.52(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
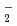 anions by high-resolution ESR spectroscopy in
anions by high-resolution ESR spectroscopy in  -ray irradiated quantum solid parahydrogen at 4.2K
-ray irradiated quantum solid parahydrogen at 4.2KKumada, Takayuki; Inagaki, Hirohisa*; Nagasawa, Takao*; Aratono, Yasuyuki; Miyazaki, Tetsuo*
Chemical Physics Letters, 251(3-4), p.219 - 222, 1996/03
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:59.87(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
J.-S.Yang*; J.-H.Kim*; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Kume, Tamikazu
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 48(6), p.731 - 735, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:54.42(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
; Takehisa, Masaaki
Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 47(2), p.359 - 363, 1983/00
no abstracts in English

 radical
radical; T.Gillbro*
J.Phys.Chem., 81(18), p.1793 - 1794, 1977/00
no abstracts in English
 -ray-induced grafting
-ray-induced graftingNuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
The ion-track grafting of a vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film is necessary for preparing nanostructured hydroxide-ion conductive electrolyte membranes. A key for success here is to obtain as high graft levels as possible (for higher conductivity) in a smaller number of tracks (for improving the other membrane properties). To this end, therefore, the effect of the medium for the VBC grafting was investigated as part of our continuing effort to optimize the experimental conditions. A 25  m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60
Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60 C. A medium was a mixture of water (H
C. A medium was a mixture of water (H O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H
O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H
O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H O.
O.
Yoshimura, Kimio; Zhao, Y.; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Shishitani, Hideyuki*; Yamaguchi, Susumu*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
Anion conducting polymer electrolyte membranes (AEMs) having poly 2-methyl-1-vinylimidazolium grafts were synthesized by radiation-induced graft coplymerizaiton of 2-methyl-1-vinylimidazole with styrene onto an ETFE film, followed by N-alkylation and ion exchange reactions. The excellent long-term stability of the prepared AEMs was confirmed in 1M KOH at 80 C. The graft-type AEM with an ion exchange capacity of 1.80 mmol/g showed a maximum power density of 210 mW cm
C. The graft-type AEM with an ion exchange capacity of 1.80 mmol/g showed a maximum power density of 210 mW cm in a direct hydrazine hydrate fuel cell test. The contrast variation experiment in small-angle neutron scattering measurement displayed the advantageous three-phase structures, consisting of crystalline, amorphous hydrophobic, and amorphous hydrophilic domains.
in a direct hydrazine hydrate fuel cell test. The contrast variation experiment in small-angle neutron scattering measurement displayed the advantageous three-phase structures, consisting of crystalline, amorphous hydrophobic, and amorphous hydrophilic domains.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
Heavy ions at kinetic energies typically from several hundreds of MeV to a few GeV passing through a polymer substrate induce a continuous trail of excitations and ionizations called latent tracks. We used a direct ion-track grafting method for preparation of anion exchange membranes for fuel cells. The functional anion exchange groups were introduced inside the latent tracks, thereby achieving OH -conductive channels through the thickness. These straight channels increased conductivities, while the isolated cylindrical structure of tracks restricted the water uptake.
-conductive channels through the thickness. These straight channels increased conductivities, while the isolated cylindrical structure of tracks restricted the water uptake.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Asano, Masaharu*; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
We investigated the ion-track grafting of vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-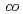 -tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film using different grafting media for applications as anion exchange membranes for fuel cells. In an attempt to increase the grafting yield, we applied a poor solvent system as the grafting medium,
-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film using different grafting media for applications as anion exchange membranes for fuel cells. In an attempt to increase the grafting yield, we applied a poor solvent system as the grafting medium,  , a mixture of water and isopropyl alcohol (H
, a mixture of water and isopropyl alcohol (H O-
O-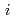 PrOH mixture). The optimum H
PrOH mixture). The optimum H O-
O-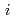 PrOH composition was identified by the kinetic parameters including the initial polymerization rate (r
PrOH composition was identified by the kinetic parameters including the initial polymerization rate (r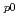 ), the radical recombination rate (
), the radical recombination rate ( ) and the grafting efficiency (r
) and the grafting efficiency (r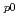 /
/ ). These parameters changed depending on the VBC-grafting/chain-transfer reaction competition for the radicals on ETFE and the Trommsdorff effect; the swelling of the grafting substrate gave an additional effect.
). These parameters changed depending on the VBC-grafting/chain-transfer reaction competition for the radicals on ETFE and the Trommsdorff effect; the swelling of the grafting substrate gave an additional effect.
Nuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Asano, Masaharu*; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
We have used the ion-track grafting technique for developing an anion exchange membrane for fuel cell applications. In order to obtain the membrane, a vinyl benzyl chloride (VBC) was grafted into an ion-irradiated poly(ethylene-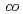 -tetrafluoroethylene) film. This study deals with investigation of the radicals remaining in each track and the VBC grafting with a variety of ion beams from the TIARA cyclotron. The accelerated ions with different masses and energies enabled us to clarify the effect of the LET and radial dose distribution in the track on the VBC grafting. Such extensive research will bring us interesting knowledge relating the track structures to the resulting membrane properties.
-tetrafluoroethylene) film. This study deals with investigation of the radicals remaining in each track and the VBC grafting with a variety of ion beams from the TIARA cyclotron. The accelerated ions with different masses and energies enabled us to clarify the effect of the LET and radial dose distribution in the track on the VBC grafting. Such extensive research will bring us interesting knowledge relating the track structures to the resulting membrane properties.